Home / News / Industry News / Steam drum: the heart and soul of natural circulation drum boiler
- Overview
- Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)
- Chemical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)
- Medical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)
-

-
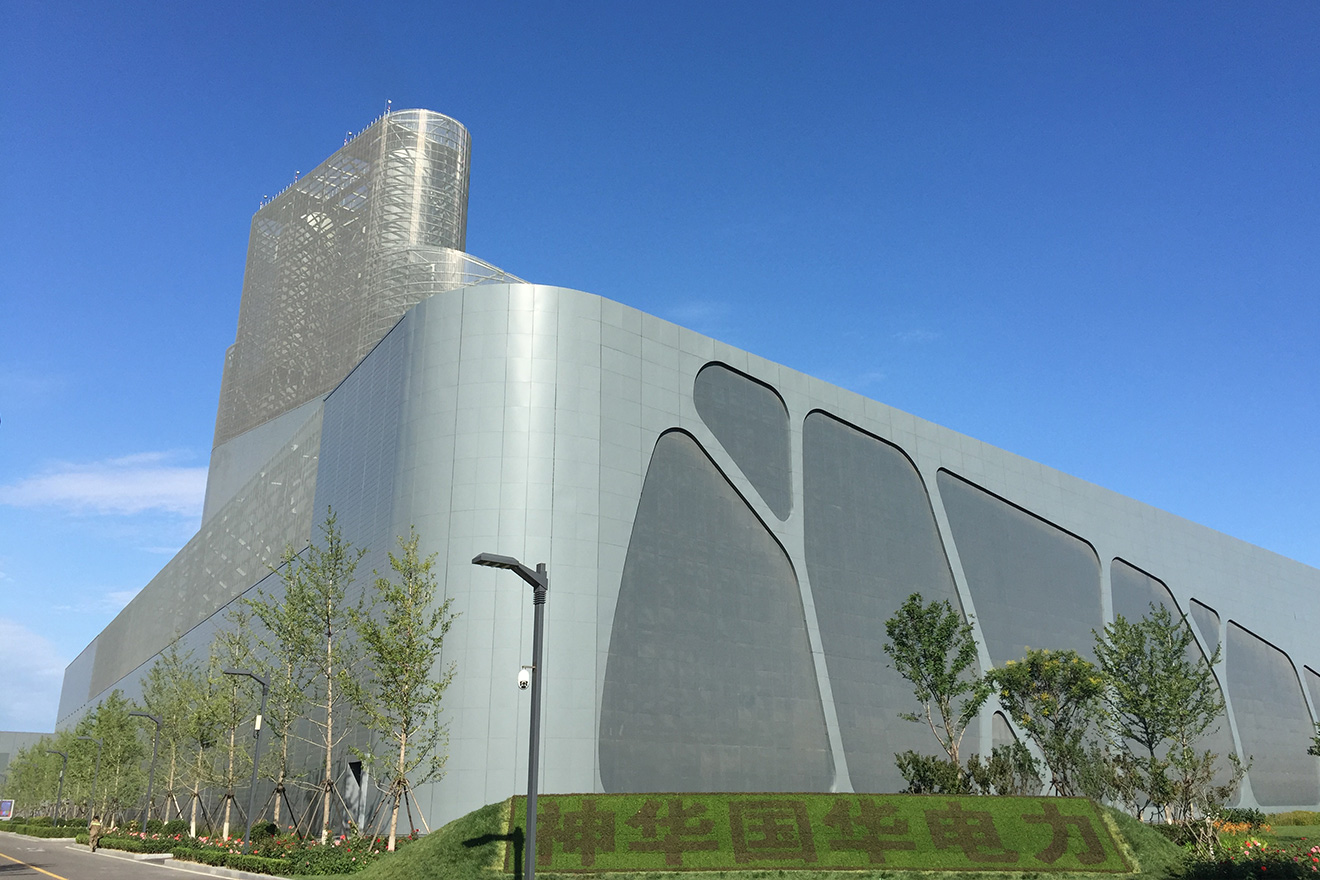
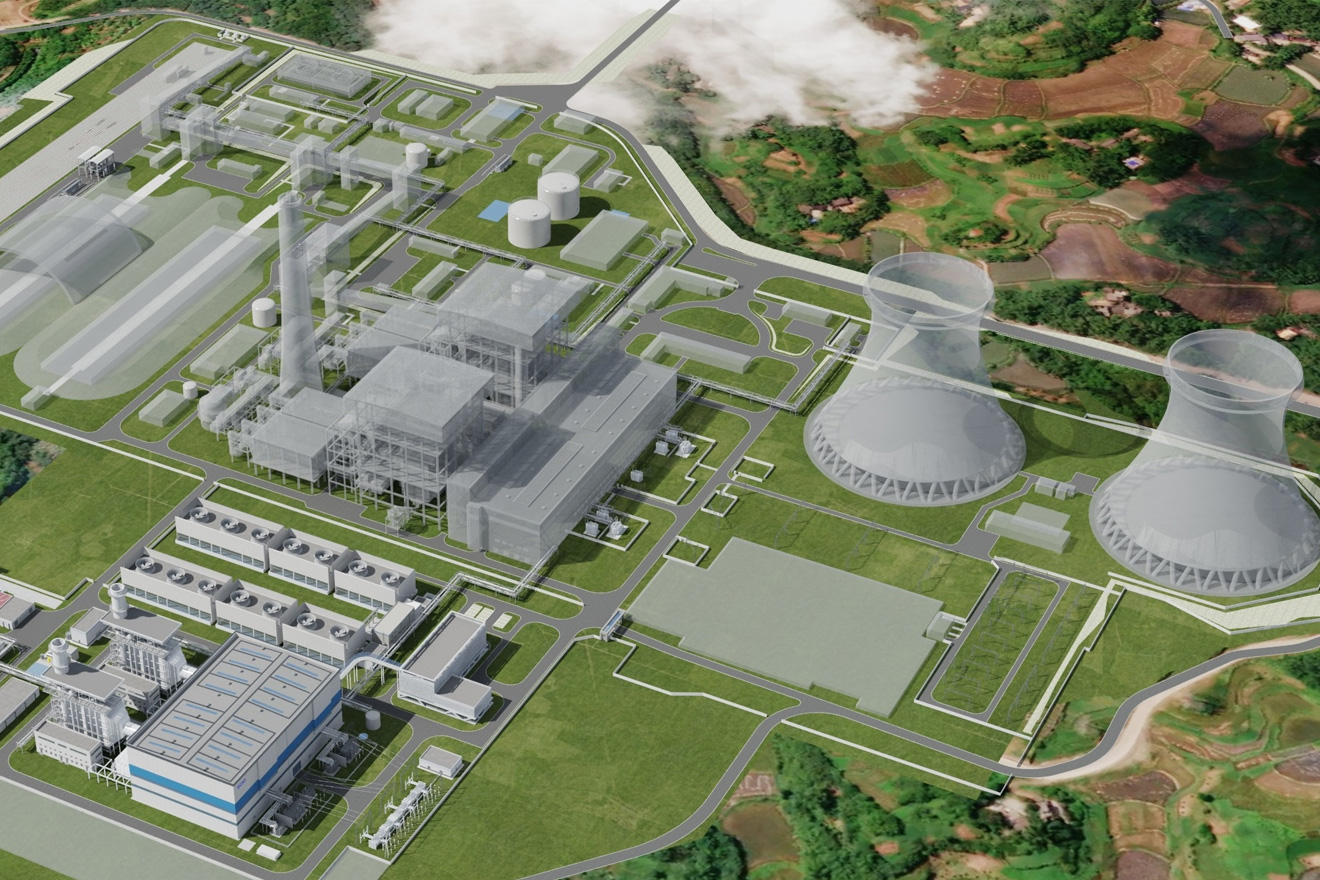 H/J class HRSG BoilerMHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB) is proud to launch its carefully crafted H/J class HRSG p...
H/J class HRSG BoilerMHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB) is proud to launch its carefully crafted H/J class HRSG p... -
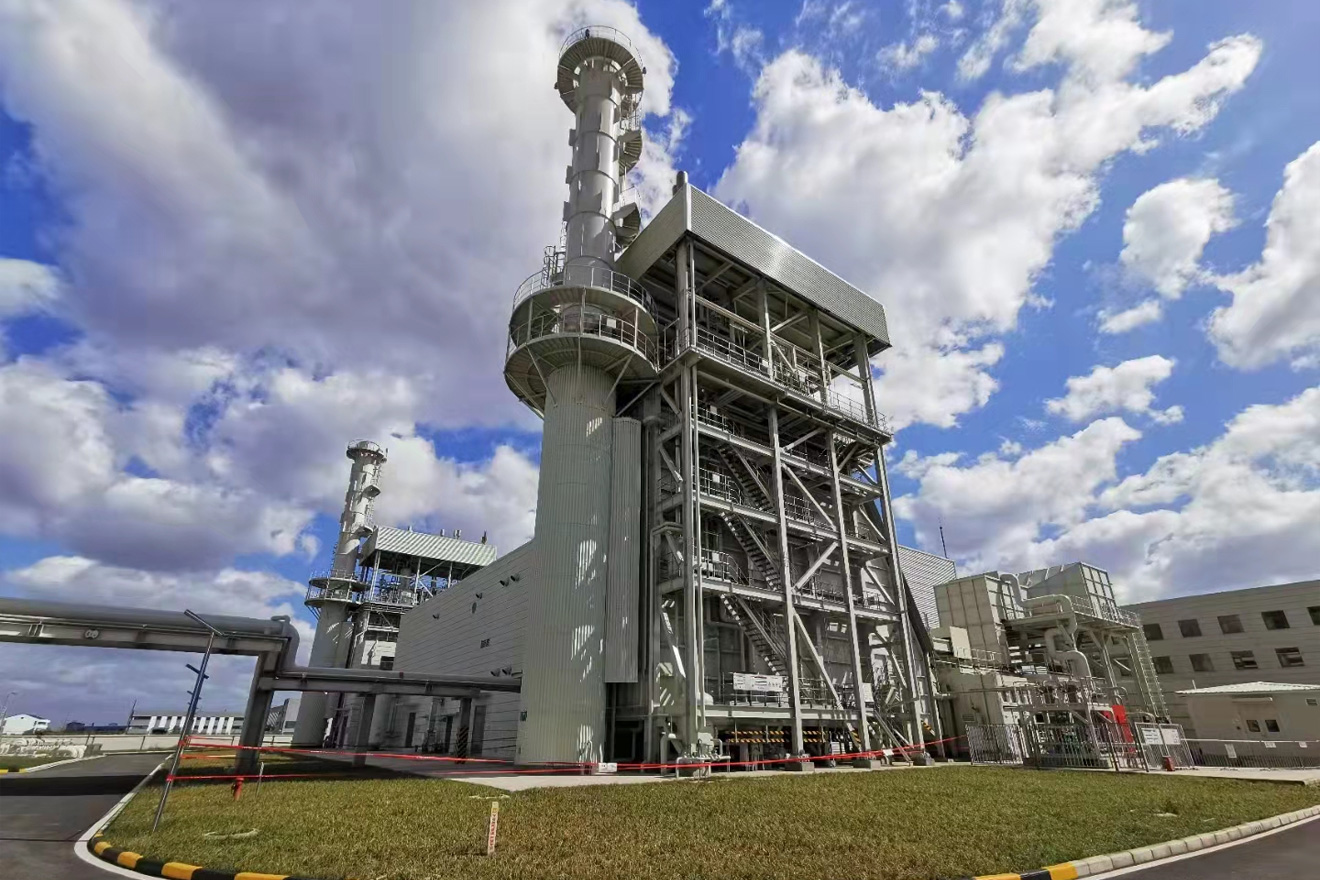
 F class HRSG BoilerThe F class HRSG, ingeniously built by MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), has become a lead...
F class HRSG BoilerThe F class HRSG, ingeniously built by MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), has become a lead... -
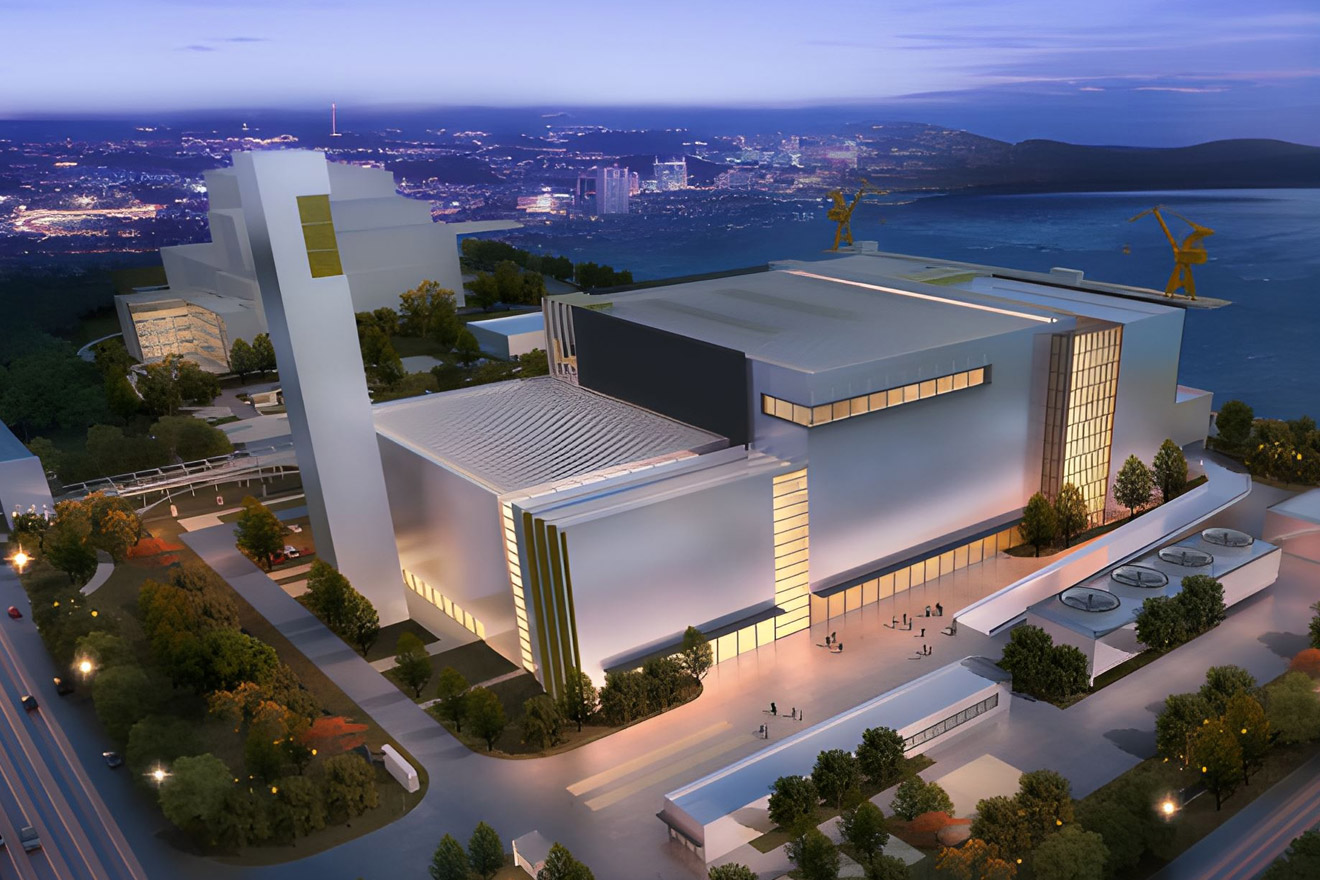
 E class & below HRSG BoilerUsing advanced convection and radiation heat transfer technology, the layout of the heating surface ...
E class & below HRSG BoilerUsing advanced convection and radiation heat transfer technology, the layout of the heating surface ...
-
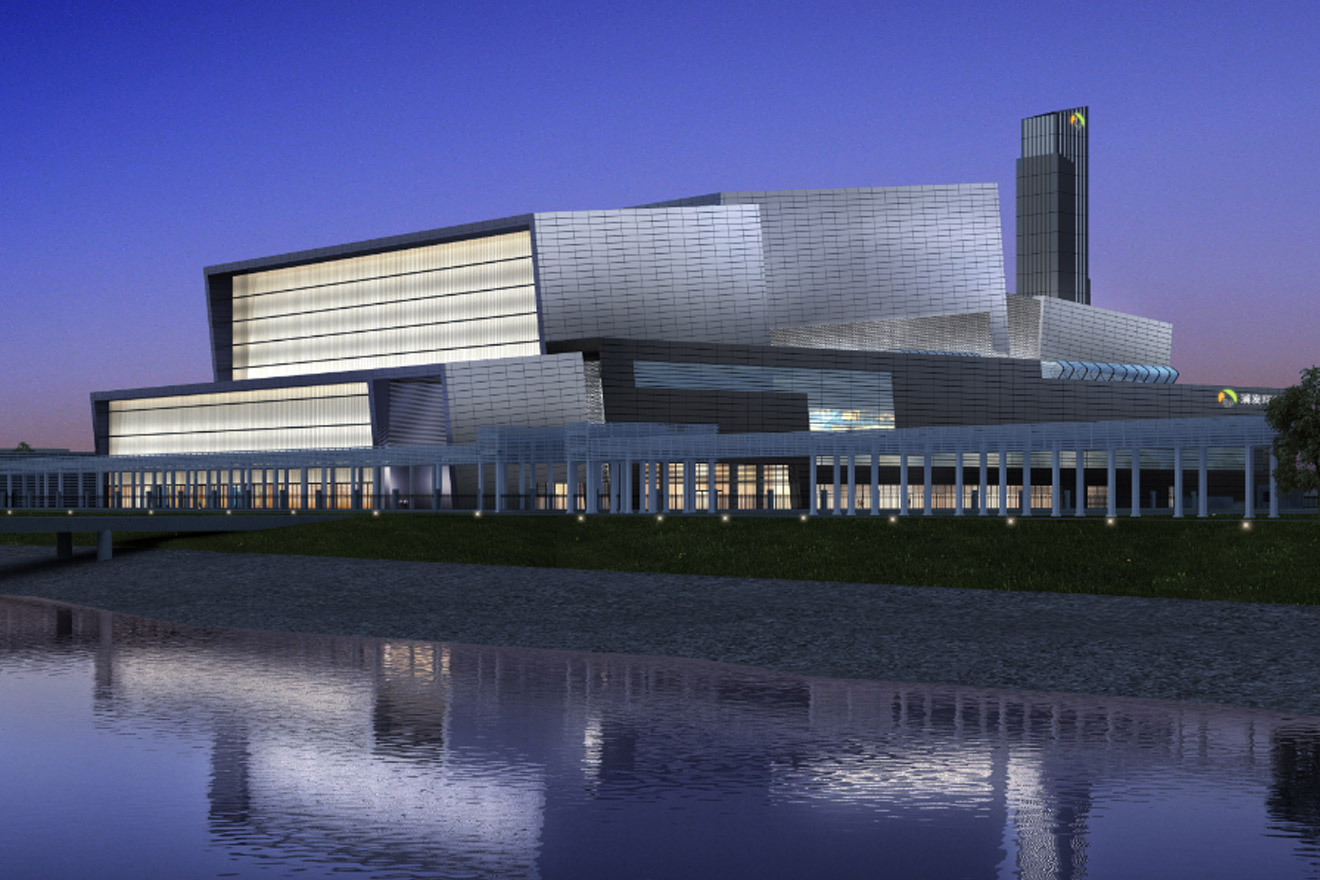
 Waste to Energy (WtE)- Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Boiler- Chemical Waste incineration Boiler- Medical Waste Incineration Boiler
Waste to Energy (WtE)- Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Boiler- Chemical Waste incineration Boiler- Medical Waste Incineration Boiler -
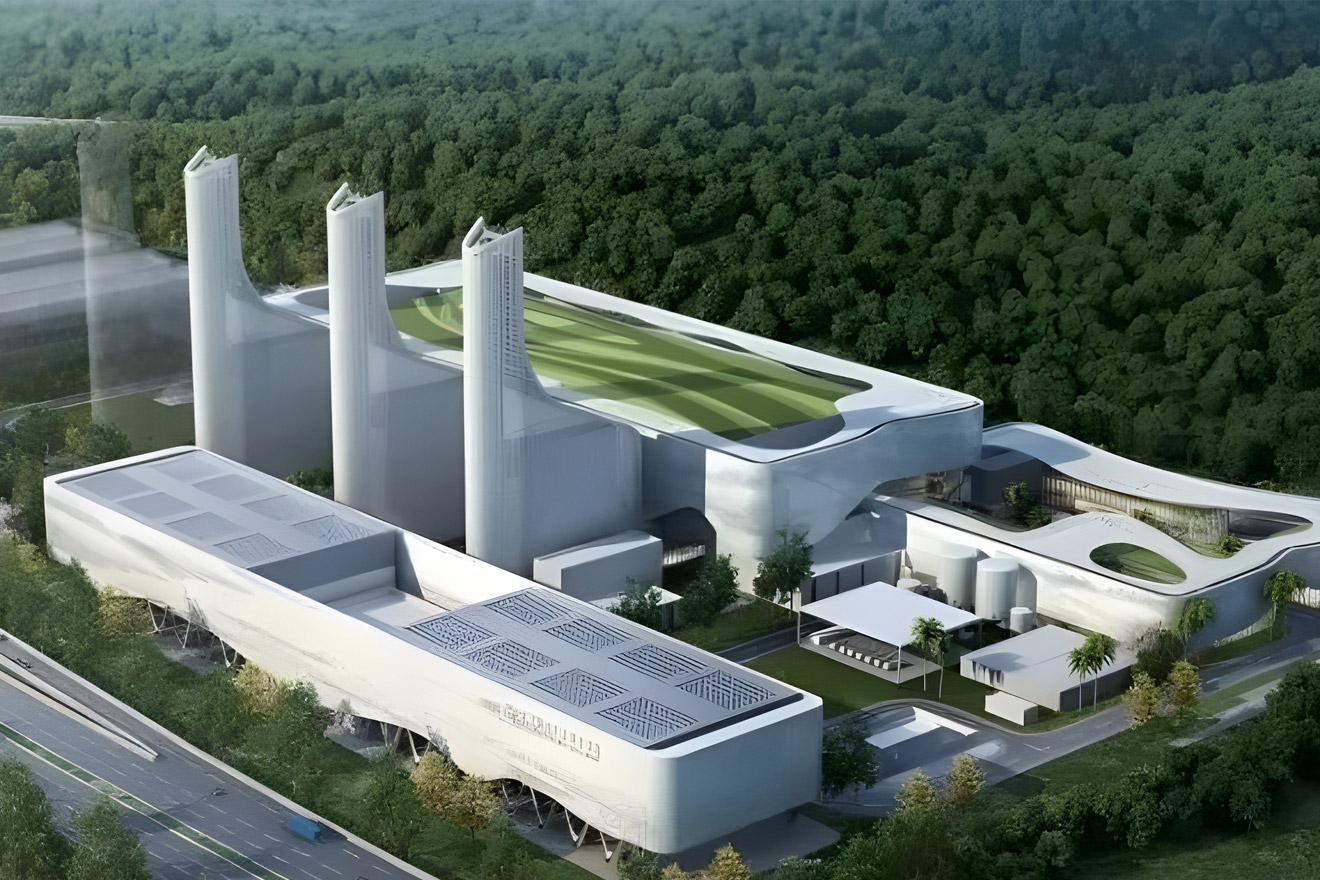
 Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)The municipal solid waste incineration boiler system professionally developed and produced by MHl Po...
Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)The municipal solid waste incineration boiler system professionally developed and produced by MHl Po... -
 Chemical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leading company in the field of hazardous chemical ...
Chemical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leading company in the field of hazardous chemical ... -
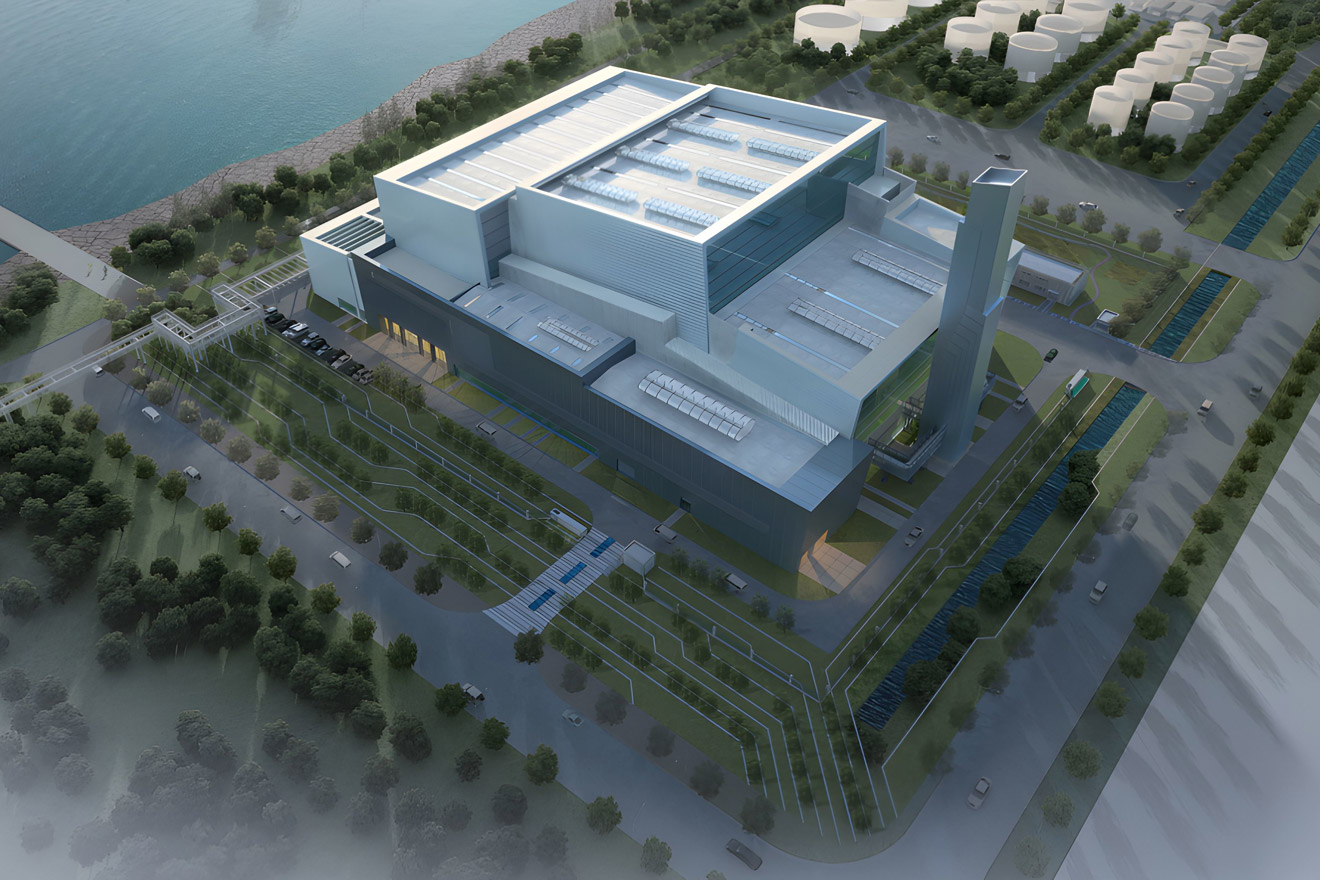 Medical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB) has carefully built a professional medical waste incinera...
Medical Waste Incineration Boiler (WtE)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB) has carefully built a professional medical waste incinera...
-
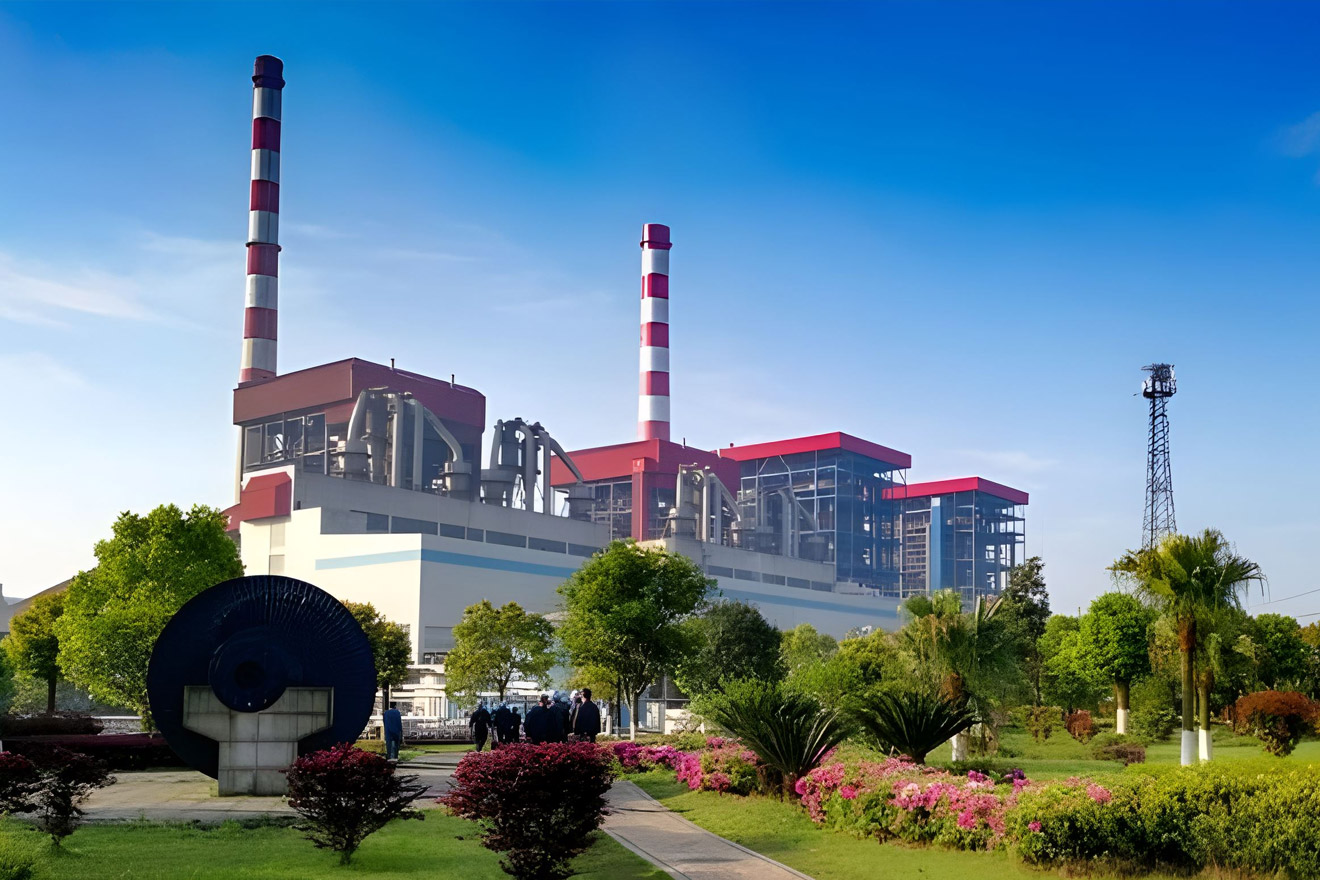 Other Boiler- Benson Once-through Boiler- Natural Circulation Drum Boiler - Special Boiler
Other Boiler- Benson Once-through Boiler- Natural Circulation Drum Boiler - Special Boiler -
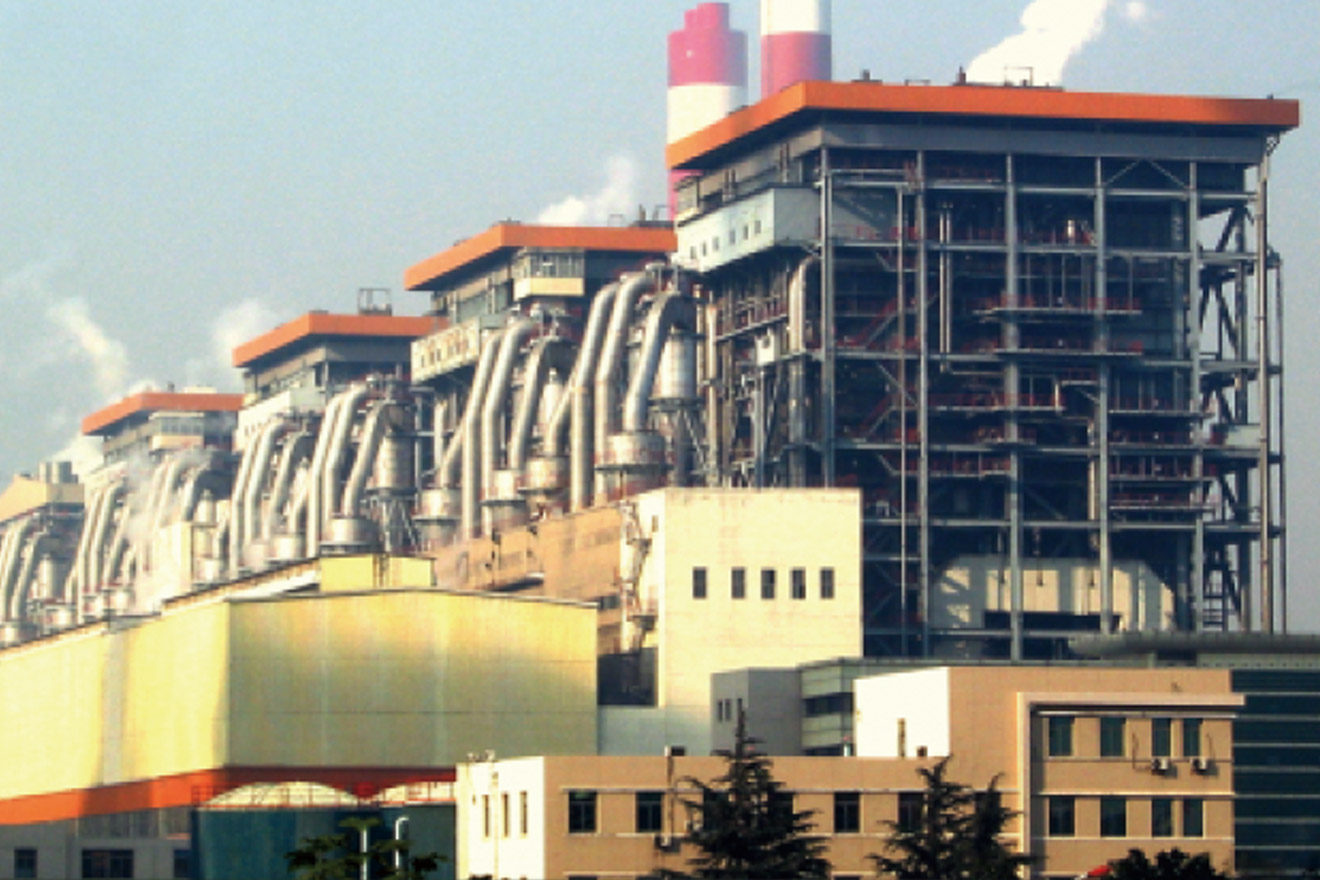 Benson Once-through Boiler (300MW and Above)Benson Once-through Boiler (300MW and Above) use advanced direct-flow combustion technology, and ach...
Benson Once-through Boiler (300MW and Above)Benson Once-through Boiler (300MW and Above) use advanced direct-flow combustion technology, and ach... -
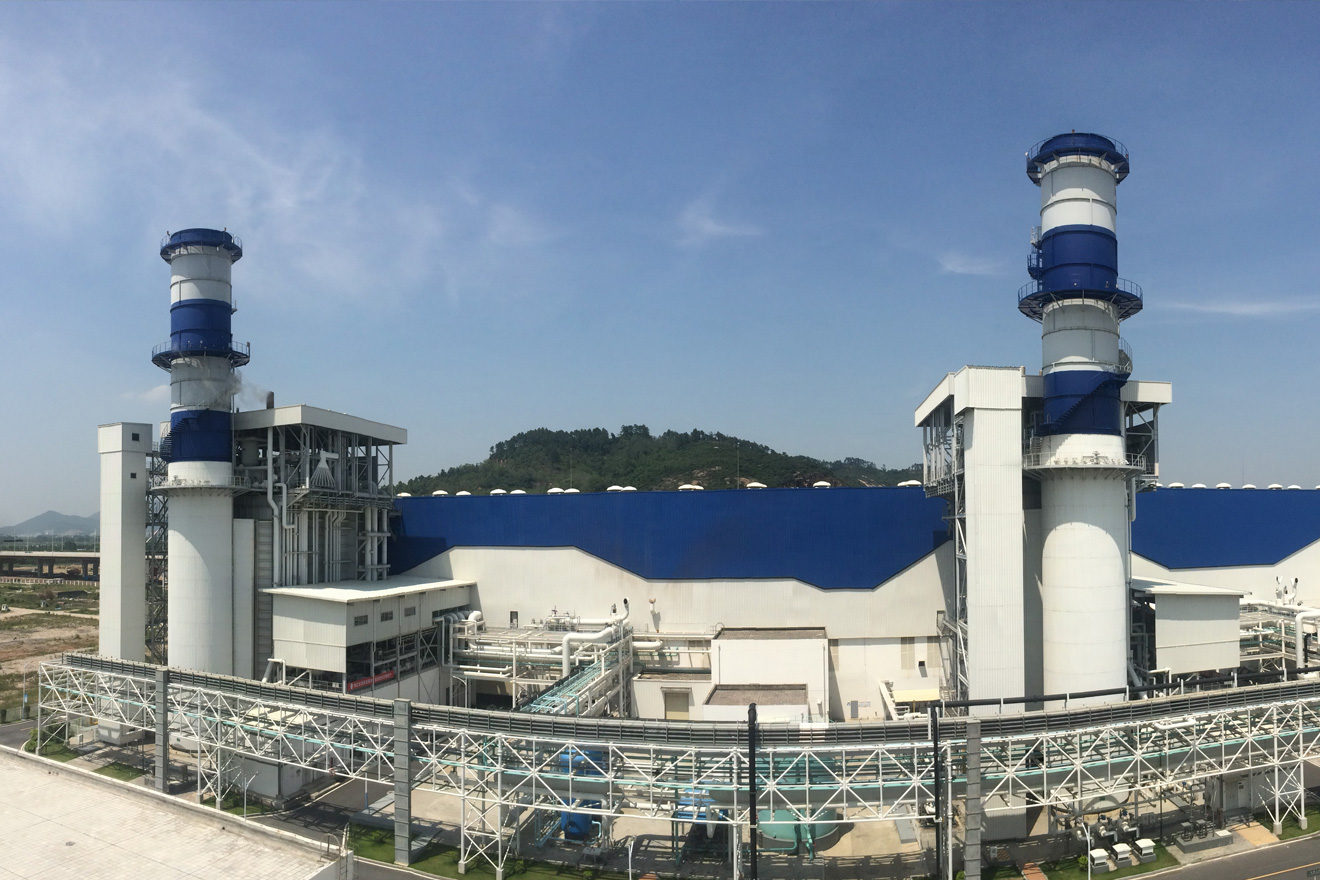
 Natural Circulation Drum Boiler (200MW and Below)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leader in energy equipment manufacturing, focuses o...
Natural Circulation Drum Boiler (200MW and Below)MHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leader in energy equipment manufacturing, focuses o... -
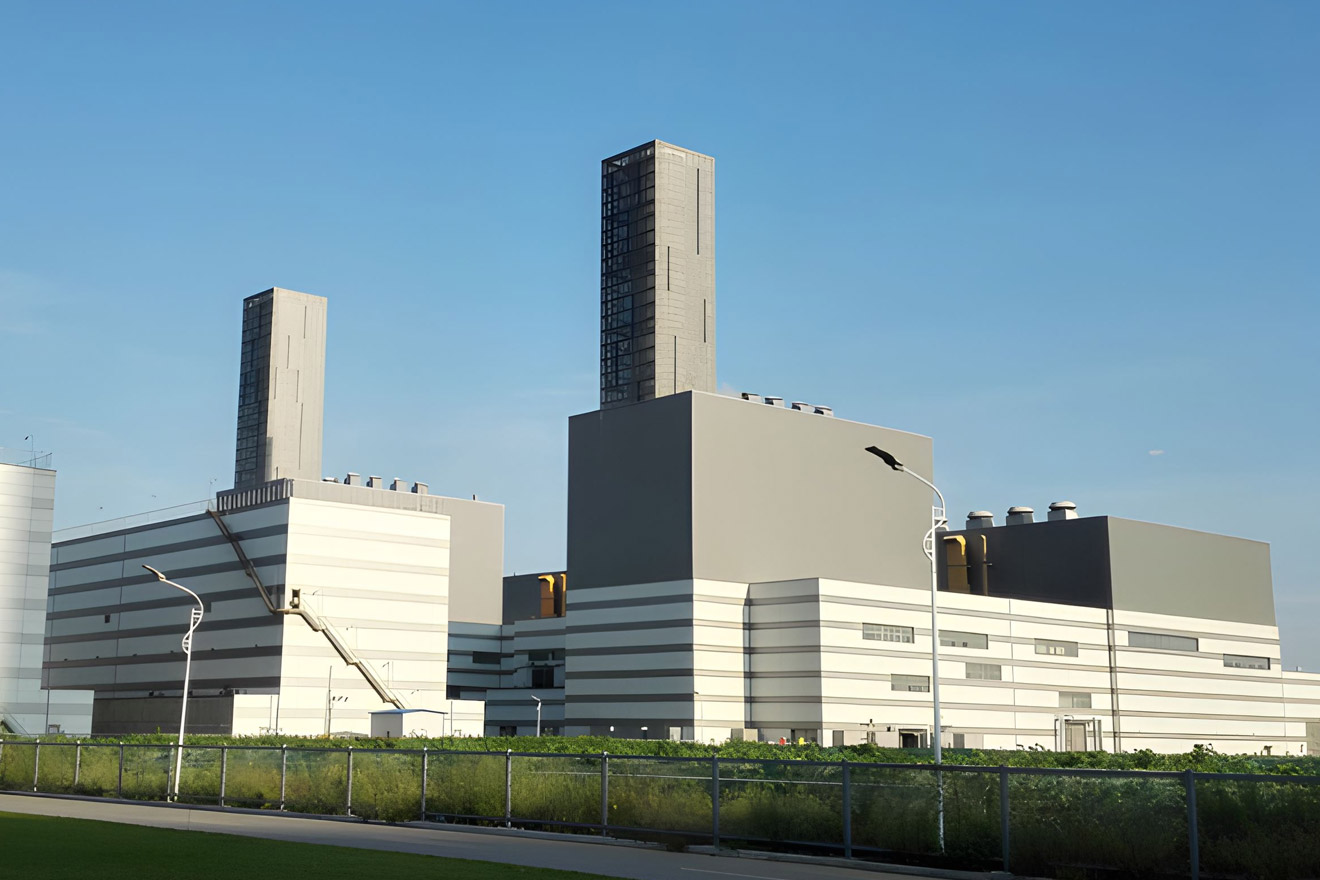 Special BoilerMHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leading manufacturer in the field of Special Boiler...
Special BoilerMHl Power Dongfang Boiler Co., Ltd. (MHDB), as a leading manufacturer in the field of Special Boiler...
-
 Service - Power UpratingH-type finned tube adopted flash resistance welding technology, welding two square steel plates with circular arc gaps in the middle to the bare tube.H-type finned tube has following characteristices:-Excellent heat transfer efficiency-small flow resistance of flue gas-Good antifly ash wear resistan...
Service - Power UpratingH-type finned tube adopted flash resistance welding technology, welding two square steel plates with circular arc gaps in the middle to the bare tube.H-type finned tube has following characteristices:-Excellent heat transfer efficiency-small flow resistance of flue gas-Good antifly ash wear resistan... -
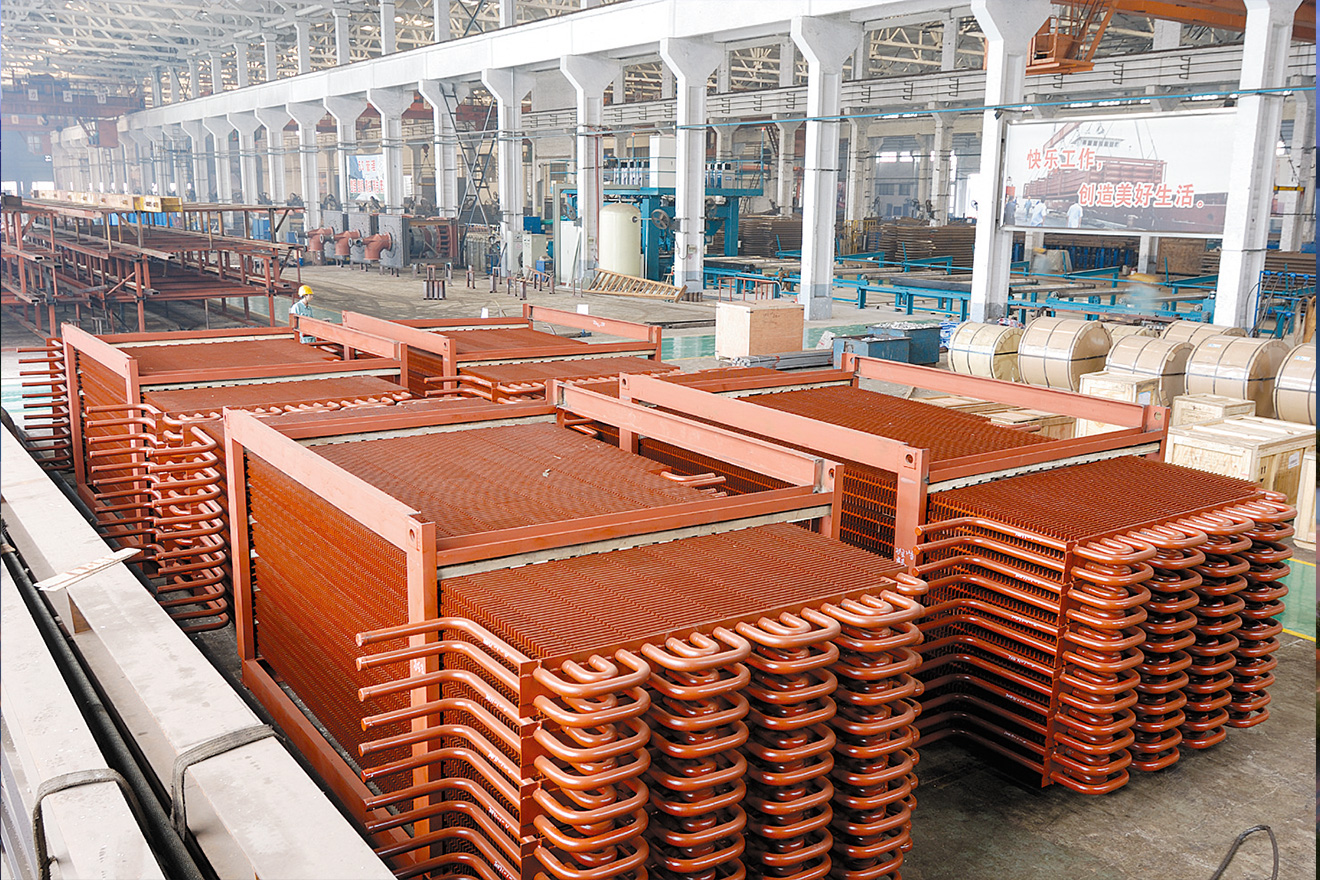 H-type Finned TubeH-type finned tube adopted flash resistance welding technology, welding two square steel plates with...
H-type Finned TubeH-type finned tube adopted flash resistance welding technology, welding two square steel plates with...

 En
En  中文简体
中文简体